Architecture details are important to understand how and why certain building elements are constructed the way they are.
If you are a young architect, such architectural details may seem foreign to you. Your school may or may not teach you these important information.
In this post, I share the top 5 (must-know) architectural details, where I believe that all young architects-to-be must start to understand and specify in their design.
Read on to see which details made it to my list.
Using the CCR Strategy
In this post, I will use the CCR Strategy to explain the details.
Components
Components refers to the various ‘layers’ or ‘parts’ that make up the whole system.
Sometimes these components are inter-dependent or totally independent.
Things to note while considering components include sequence, interfacing and material properties.
Concept
Concept refers to the design considerations that architectural designers should know about the system. This could include having set dimensions or thickness or the right sequence of layers for RC flat roofs.
Rationale
Rationale refers to the reason and purpose of having the above mentioned components and concepts for the particular building element. For example, the railing height must be above 1m to prevent fall from height along staircases.
RC Flat Roof

Components:
- Slab, min 25mm cement & sand screed to fall, 1.5mm thk waterproofing membrane, 50mm thk insulation, 50mm thk precast panels)
Concepts:
- Total finishes thickness = 150mm thk min.
- Difference btwn screed to fall vs structural fall
Rationale:
- Provide insulation, waterproofing and screed to fall for drainage
Parapet Wall & Coping

Components:
- Drip edge, Coping/flashing
Concepts:
- 13mm wide drip edge
- 3-5 deg fall for coping inwards
- Material of coping = Concrete / Metal
Rationale:
- To prevent staining of external wall from rainwater.
Door & Window

Components:
Architrave, laminate panel, door frame & ironmongery
Concept:
- Establish clear width & height for doors and windows
- Check door swing direction and clearance of nearby corridors
Rationale:
- Ensure safe passage & adaquate space for people for fire escape and/or equipment to pass through.
Railing & Staircase
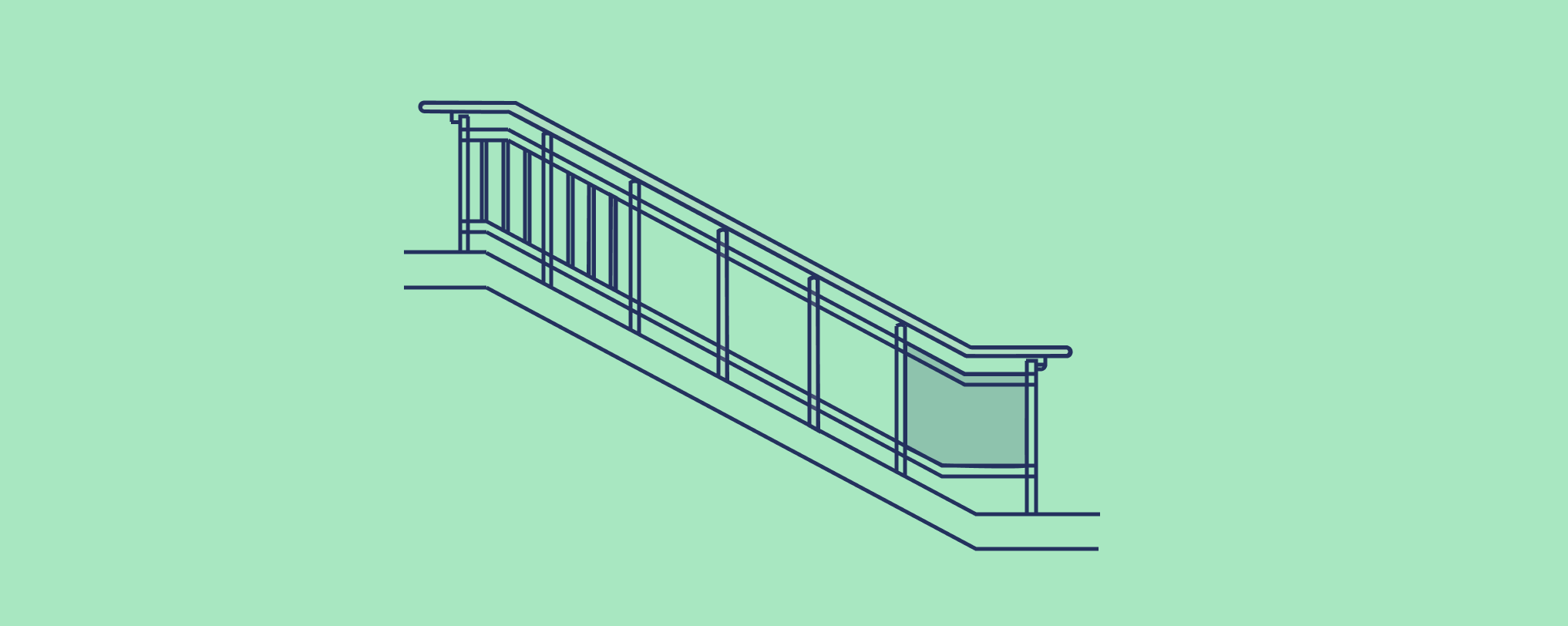
Components:
Balsatrades, Posts, bottom rail/kerb, handrail extension, height of raiiing, clear width between railings, supports
Concept:
- Establish height of railing,
- Establish clear width of staircase, landing, tread and riser of staircase
Rationale:
- Ensure safe passage through staircase, and prevent falls at edges of building.
Learn more about staircase design basics.
Waterproofing

Components:
Waterproofing membrane (surface or liquid-applied), concrete additives or waterproofing concrete.
Concept:
- Located at wet areas, parapet wall, shower area, pipe openings, under slab with upturn or downturn where neccessary (typically 300mm floor slabs or 1800mm for shower areas)
Rationale:
- To prevent water from entering the concrete structure and degrading it.
Conclusion
The list above are what I feel are what architectural designers and students should be familiar with. Do consult your firms detail library and spend some time identifying the components, rationale for each detail. Happy learning!
.png)





